BANDGAP: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
[[The_VASP_Manual|Contents]] | [[The_VASP_Manual|Contents]] | ||
[[Category:INCAR tag]][[Category:Electronic Minimization]][[Category:Density of States]] | <!-- Commented out until public [[Category:INCAR tag]][[Category:Electronic Minimization]][[Category:Density of States]] --> | ||
Revision as of 12:21, 17 October 2023
BANDGAP = COMPACT | WEIGHT | KPOINT
Default: BANDGAP = COMPACT
Description: BANDGAP determines the verbosity for reporting the bandgap to the OUTCAR file.
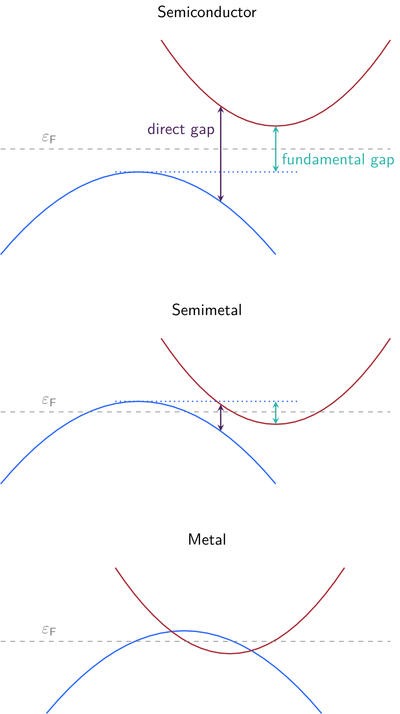
The bandgap of the system separates the occupied valence bands from the unoccupied conduction bands. Of particular interest are the fundamental bandgap between valence band maximum (VBM) and conduction band minimum (CBM) and the direct bandgap at a single k point.
BANDGAP controls how VASP reports the bandgap information. The following options exist:
- BANDGAP=COMPACT
- Uses Fermi weights to decide what valence and conduction bands are. Reports the VBM, CBM, and fundamental gap to the OUTCAR file.
- BANDGAP=WEIGHT
- Uses Fermi weights to decide what valence and conduction bands are. Provides a comprehensive report of all band extrema.
- BANDGAP=KPOINT
- Considers each k point individually to decide what valence and conduction bands are. Provides a comprehensive report of all band extrema.
Related tags and articles
