Category:Pseudopotentials: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Sketch Pseudopotentials.png|300px|right|Sketch of a pseudopotential and pseudowavefunction]] | [[File:Sketch Pseudopotentials.png|300px|right|Sketch of a pseudopotential and pseudowavefunction]] | ||
'''Pseudopotentials''', or effective potentials, are well-behaved potentials that replace the ionic potentials | '''Pseudopotentials''', or effective potentials, are well-behaved potentials that replace the diverging ionic potentials. As a result, the [[Pseudopotential_basics|pseudopotential approach]] significantly speeds up [[Electronic_minimization|electronic structure calculations]] and makes the simulation of a wider range of materials feasible. | ||
In a nutshell: | |||
* The pseudopotential and associated information required for a calculation must be present in a {{FILE|POTCAR}} file. | |||
* Simple instructions to set up a {{FILE|POTCAR}} file with the correct format: [[Preparing a POTCAR]]. | |||
* Guide on recommendations: [[Choosing pseudopotentials]]. | |||
* Overview of all versions and nomenclature: [[Available pseudopotentials]] | |||
==Theory== | |||
VASP employs the [[projector-augmented-wave formalism|projector-augmented-wave (PAW) method]] that uses a plane-wave basis. A plane-wave basis is most convenient for periodic systems, however without the help of '''pseudopotentials''' the description of oscillations near the nuclei (nodal features) would necessitate an excessively high number of plane waves. The PAW method introduces a mixed basis where the Kohn-Sham (KS) orbitals are decomposed in three contributions: The pseudo orbitals, pseudo-onsite orbitals and all-electron onsite orbitals. The PAW potentials and resulting pseudo orbitals are identical to the true ionic potentials and KS orbitals outside a specific radius, as illustrated in the figure. These pseudo orbitals contain no nodal features and are, thus, given in a plane-wave basis. Inside the PAW spheres the nodal features are reintroduced on a radial logarithmic grid by subtracting the pseudo-onsite orbitals and adding the all-electron onsite orbitals. | |||
An additional approximation taken alongside the pseudopotential method is the ''frozen-core approximation''. Here, the electrons associated with an ion are separated into valence electrons ({{TAG|ZVAL}}) that are assumed to take part in the physical/chemical property of interest and core electrons that are included as screening of the ionic potential. The separation into valence and core states depends on the property of interest and chemical bonds that occur for a specific material. For a specific atom type, VASP has a range of [[available pseudopotentials|available pseudopotentials]] that vary in terms of core radius, the number of valence electrons, their ability to describe excited states, etc. | |||
The plane-wave coefficients of the pseudo orbitals are associated with reciprocal vectors <math>\mathbf{G}</math> in Fourier space. The number of Fourier components determines the computational cost and can be controlled by the cutoff energy ({{TAG|ENCUT}}). The appropriate value depends on the pseudopotential and other factors. A potential is considered ''soft'' when few Fourier components are sufficient for an accurate representation, and ''hard'' otherwise. It is expedient to perform a convergence study on {{TAG|ENCUT}} with respect to the quantity of interest. | |||
[[Category:Calculation setup]] | |||
Revision as of 08:07, 13 June 2024
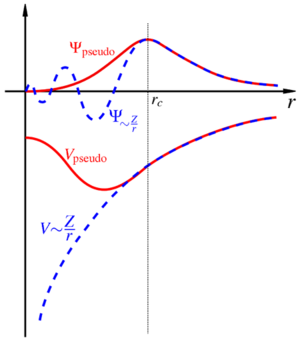
Pseudopotentials, or effective potentials, are well-behaved potentials that replace the diverging ionic potentials. As a result, the pseudopotential approach significantly speeds up electronic structure calculations and makes the simulation of a wider range of materials feasible.
In a nutshell:
- The pseudopotential and associated information required for a calculation must be present in a POTCAR file.
- Simple instructions to set up a POTCAR file with the correct format: Preparing a POTCAR.
- Guide on recommendations: Choosing pseudopotentials.
- Overview of all versions and nomenclature: Available pseudopotentials
Theory
VASP employs the projector-augmented-wave (PAW) method that uses a plane-wave basis. A plane-wave basis is most convenient for periodic systems, however without the help of pseudopotentials the description of oscillations near the nuclei (nodal features) would necessitate an excessively high number of plane waves. The PAW method introduces a mixed basis where the Kohn-Sham (KS) orbitals are decomposed in three contributions: The pseudo orbitals, pseudo-onsite orbitals and all-electron onsite orbitals. The PAW potentials and resulting pseudo orbitals are identical to the true ionic potentials and KS orbitals outside a specific radius, as illustrated in the figure. These pseudo orbitals contain no nodal features and are, thus, given in a plane-wave basis. Inside the PAW spheres the nodal features are reintroduced on a radial logarithmic grid by subtracting the pseudo-onsite orbitals and adding the all-electron onsite orbitals.
An additional approximation taken alongside the pseudopotential method is the frozen-core approximation. Here, the electrons associated with an ion are separated into valence electrons (ZVAL) that are assumed to take part in the physical/chemical property of interest and core electrons that are included as screening of the ionic potential. The separation into valence and core states depends on the property of interest and chemical bonds that occur for a specific material. For a specific atom type, VASP has a range of available pseudopotentials that vary in terms of core radius, the number of valence electrons, their ability to describe excited states, etc.
The plane-wave coefficients of the pseudo orbitals are associated with reciprocal vectors in Fourier space. The number of Fourier components determines the computational cost and can be controlled by the cutoff energy (ENCUT). The appropriate value depends on the pseudopotential and other factors. A potential is considered soft when few Fourier components are sufficient for an accurate representation, and hard otherwise. It is expedient to perform a convergence study on ENCUT with respect to the quantity of interest.
Subcategories
This category has the following 2 subcategories, out of 2 total.
Pages in category "Pseudopotentials"
The following 5 pages are in this category, out of 5 total.
