Pulay stress: Difference between revisions
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
As mentioned previously, <math>N_{PW}</math> is constant in a relaxation calculation, which means that <math>E_{cutoff}</math> must change to compensate for changes in <math>\Omega</math>. This is illustrated in Fig. 2. At the start, the initial G-vectors within a sphere are included within the basis. When the cell volume increases (<math>V_1 < V_2</math>), the number of G-vectors in reciprocal space remains constant, but their length increases. This effectively results in a change of basis, leading to (<math>E_{cutoff,1} > E_{cutoff,2}</math>). This basis remains constant for the duration of the relaxation. However, if the calculation is then restarted, the basis is reset. This means that the number of G-vectors is greater for the larger real space cell. One effect of this is that the real-space grid increases in points as their spacing remains constant but there is more space for them to fill. However, the corresponding reciprocal space decreases, as can be seen in the lower half of Fig. 2. | As mentioned previously, <math>N_{PW}</math> is constant in a relaxation calculation, which means that <math>E_{cutoff}</math> must change to compensate for changes in <math>\Omega</math>. This is illustrated in Fig. 2. At the start, the initial G-vectors within a sphere are included within the basis. When the cell volume increases (<math>V_1 < V_2</math>), the number of G-vectors in reciprocal space remains constant, but their length increases. This effectively results in a change of basis, leading to (<math>E_{cutoff,1} > E_{cutoff,2}</math>). This basis remains constant for the duration of the relaxation. However, if the calculation is then restarted, the basis is reset. This means that the number of G-vectors is greater for the larger real space cell. One effect of this is that the real-space grid increases in points as their spacing remains constant but there is more space for them to fill. However, the corresponding reciprocal space decreases, as can be seen in the lower half of Fig. 2. | ||
Contrastingly, when the volume decreases on relaxation (<math>V_1 < V_2</math>), the length of the constant number of G-vectors decreases. The effective cutoff should increase but the number of grid points effectively decreases, so it does not change???? If the calculation restarts, the basis is reset, so the number of G-vectors is less for the smaller real space cell. The number of real space grid points decreases, so the number of reciprocal space grid points increases. AND this also changes the length??? | Contrastingly, when the volume decreases on relaxation (<math>V_1 < V_2</math>), the length of the constant number of G-vectors decreases. The effective <math>E_{cutoff}</math> should increase but the number of grid points effectively decreases, so it does not change???? If the calculation restarts, the basis is reset, so the number of G-vectors is less for the smaller real space cell. The number of real space grid points decreases, so the number of reciprocal space grid points increases. AND this also changes the length??? | ||
Revision as of 12:16, 29 July 2024
Pulay stress is unphysical stress resulting from unconverged calculations with respect to basis set. It distorts the cell structure, decreasing it from the equilibrium volume and creating difficulties in volume relaxation. The resultant energy vs. volume curves, cf. Figure 1 (top), are jagged and special care must be taken to obtain reasonable structures, cf. volume relaxation PAGE-LINK. In this article, the computational origin of this is discussed.
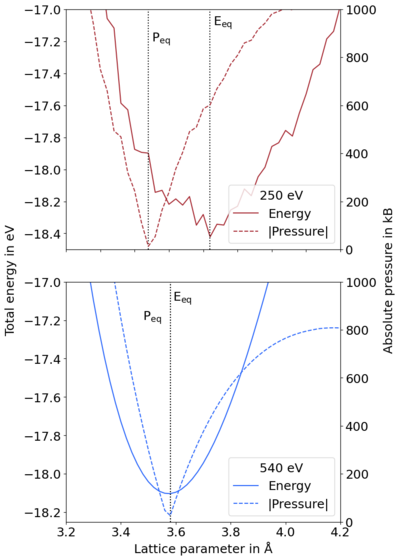
It is important to note that problems due to the Pulay stress can often be neglected if only volume-conserving relaxations are performed. This is because the Pulay stress is, usually, nearly uniform and only changes the diagonal elements of the stress tensor by a constant amount.
Introduction
The energy for a periodic system, e.g. band structures, is calculated using a finite number of plane waves and a finite number of k-points. A fixed number of plane waves or plane wave energy cutoff may be used to set a constant basis.[1] In VASP, a constant energy cutoff is used, cf. ENCUT. The number of plane waves is related to the energy cutoff and the size of the cell :
is constant in a relaxation calculation, which means that must change to compensate for changes in . All the initial G-vectors within a sphere are included in the basis. However, when comparing cells of different sizes, i.e. during a relaxation, the cell shape is relaxed, so the direct and reciprocal lattice vectors change. The number of reciprocal G-vectors in the basis is kept fixed but the length of the G-vectors changes, indirectly changing the energy cutoff. In other words, the shape of the cutoff region changes from a sphere to an ellipsoid. This can be solved by using an infinite number of k-points and plane waves. In practice, a large enough plane wave energy cutoff and number of k-points leads to converged energies.[2] All energy changes are strictly consistent with the stress tensor; however, when the basis set is too small, i.e. prematurely truncated, this results in discontinuities in the total energy between cells of varying volumes. These discontinuities between energy and volume create stress that decreases the equilibrium volume (cf. Fig. 1 (top)), due to the diagonal components of the stress tensor being incorrect. This is called the Pulay stress.
The pressure of the cell, being proportional to the trace of the stress tensor, can be used to visualize this. When the cell volume is below the equilibrium volume, the pressure is positive; contrastingly, it is negative when above the equilibrium volume, so at equilibrium, this is zero. Plotting the magnitude of the pressure vs. volume curve and the total energy allows comparison between these two minima. In Figure 1 it is clear that the the absolute pressure-volume and energy-volume minima coincide for a converged basis, while the pressure equilibrium is much lower than the energy equilibrium for the unconverged basis. This is the effect of the Pulay stress.
More detail explanation
As mentioned previously, is constant in a relaxation calculation, which means that must change to compensate for changes in . This is illustrated in Fig. 2. At the start, the initial G-vectors within a sphere are included within the basis. When the cell volume increases (), the number of G-vectors in reciprocal space remains constant, but their length increases. This effectively results in a change of basis, leading to (). This basis remains constant for the duration of the relaxation. However, if the calculation is then restarted, the basis is reset. This means that the number of G-vectors is greater for the larger real space cell. One effect of this is that the real-space grid increases in points as their spacing remains constant but there is more space for them to fill. However, the corresponding reciprocal space decreases, as can be seen in the lower half of Fig. 2.
Contrastingly, when the volume decreases on relaxation (), the length of the constant number of G-vectors decreases. The effective should increase but the number of grid points effectively decreases, so it does not change???? If the calculation restarts, the basis is reset, so the number of G-vectors is less for the smaller real space cell. The number of real space grid points decreases, so the number of reciprocal space grid points increases. AND this also changes the length???
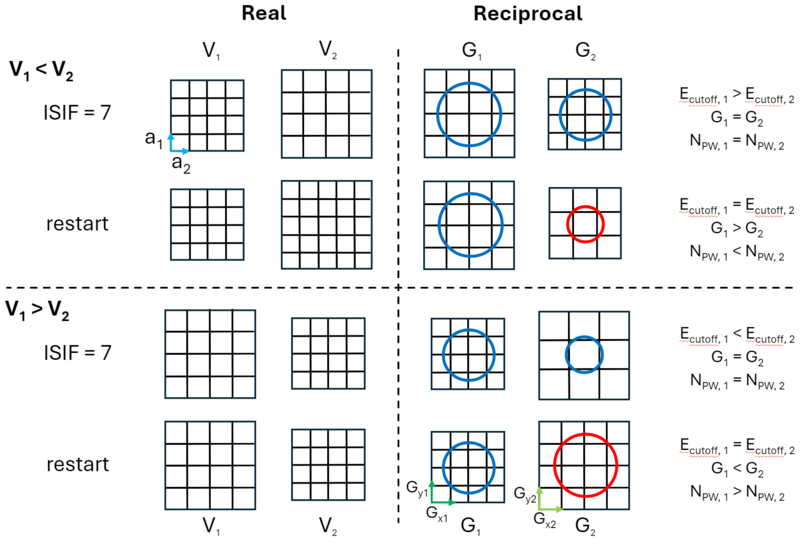
Alternatively, the shape of the cell could change. This has a significant impact on the basis. INSERT IMAGE
References
- ↑ P. Gomes Dacosta, O. Nielsen, and K. Kunc, Stress theorem in the determination of static equilibrium by the density functional method, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 19, 3163 (1986).
- ↑ G. P. Francis and M. C. Payne, Finite basis set corrections to total energy pseudopotential calculations, J. Condens. Matter Phys. 2, 4395 (1990).
