STM of graphene: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Sur_sci}} | {{Sur_sci - Tutorial}} | ||
== Task == | == Task == | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Input == | == Input == | ||
=== POSCAR === | === {{TAG|POSCAR}} === | ||
C: Graphite Lattice | C: Graphite Lattice | ||
1.0 | 1.0 | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
+0.0000000000 +1.4093387034 +0.0000000000 | +0.0000000000 +1.4093387034 +0.0000000000 | ||
=== INCAR === | === {{TAG|INCAR}} === | ||
general: | general: | ||
SYSTEM = Graphite surface slap | {{TAGBL|SYSTEM}} = Graphite surface slap | ||
ENMAX = 400 | {{TAGBL|ENMAX}} = 400 | ||
ISMEAR = 2 ; SIGMA = 0.2 | {{TAGBL|ISMEAR}} = 2 ; SIGMA = 0.2 | ||
ALGO= Fast | {{TAGBL|ALGO}} = Fast | ||
partial charge densities: | partial charge densities: | ||
LPARD = .TRUE. | {{TAGBL|LPARD}} = .TRUE. | ||
LSEPK = .FALSE. | {{TAGBL|LSEPK}} = .FALSE. | ||
LSEPB = .FALSE. | {{TAGBL|LSEPB}} = .FALSE. | ||
NBMOD = -3 | {{TAGBL|NBMOD}} = -3 | ||
EINT = -0.1 0.1 | {{TAGBL|EINT}} = -0.1 0.1 | ||
#DOS: | #DOS: | ||
#ISTART = 0 | #{{TAGBL|ISTART}} = 0 | ||
#ICHARG = 2 | #{{TAGBL|ICHARG}} = 2 | ||
#LORBIT = 11 | #{{TAGBL|LORBIT}} = 11 | ||
=== KPOINTS === | === {{TAG|KPOINTS}} === | ||
K-Points | K-Points | ||
0 | 0 | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
== Calculation == | == Calculation == | ||
*This example is carried out in complete analogy to . | *This example is carried out in complete analogy to the example {{TAG|STM of graphite}}. | ||
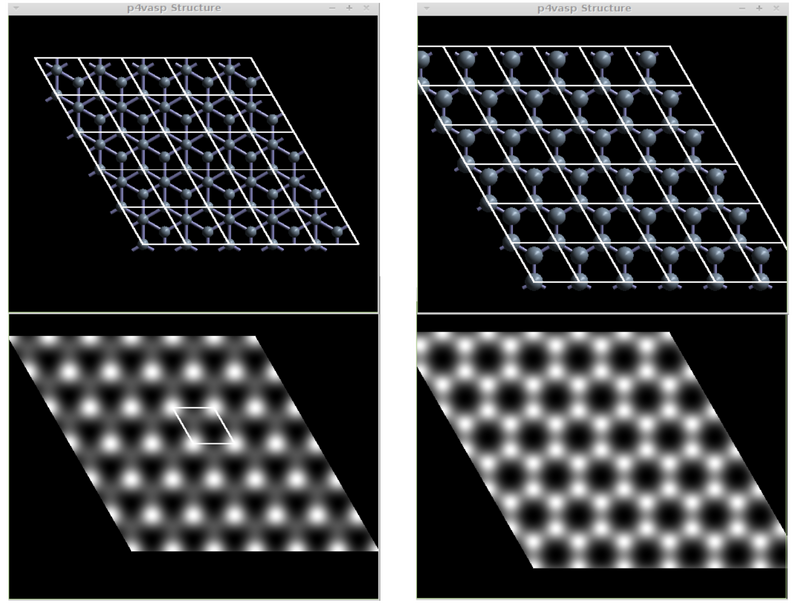
*The sample output for the graphite (left) and graphene (right) STM images should look like the following: | *The sample output for the graphite (left) and graphene (right) STM images should look like the following: | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
== Download == | == Download == | ||
[ | [[Media:Graphene_STM.tgz| Graphene_STM.tgz]] | ||
{{Sur_sci}} | |||
[[Category:Examples]] | [[Category:Examples]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:18, 14 November 2019
Overview > Ni 100 surface relaxation > Ni 100 surface DOS > Ni 100 surface bandstructure > Ni 111 surface relaxation > CO on Ni 111 surface > Ni 111 surface high precision > partial DOS of CO on Ni 111 surface > vibrational frequencies of CO on Ni 111 surface > STM of graphite > STM of graphene > collective jumps of a Pt adatom on fcc-Pt (001): Nudged Elastic Band Calculation > List of tutorials
Task
Generation of an STM image of a graphene surface.
Input
POSCAR
C: Graphite Lattice 1.0 +2.4410462393 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 -1.2205231197 +2.1140080551 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +10.0000000000 2 Cartesian +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +1.4093387034 +0.0000000000
INCAR
general: SYSTEM = Graphite surface slap ENMAX = 400 ISMEAR = 2 ; SIGMA = 0.2 ALGO = Fast partial charge densities: LPARD = .TRUE. LSEPK = .FALSE. LSEPB = .FALSE. NBMOD = -3 EINT = -0.1 0.1 #DOS: #ISTART = 0 #ICHARG = 2 #LORBIT = 11
KPOINTS
K-Points 0 Monkhorst-Pack 9 9 1 0 0 0
Calculation
- This example is carried out in complete analogy to the example STM of graphite.
- The sample output for the graphite (left) and graphene (right) STM images should look like the following:
Download
Overview > Ni 100 surface relaxation > Ni 100 surface DOS > Ni 100 surface bandstructure > Ni 111 surface relaxation > CO on Ni 111 surface > Ni 111 surface high precision > partial DOS of CO on Ni 111 surface > vibrational frequencies of CO on Ni 111 surface > STM of graphite > STM of graphene > collective jumps of a Pt adatom on fcc-Pt (001): Nudged Elastic Band Calculation > List of tutorials