O dimer: Difference between revisions
Vaspmaster (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
|||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:At_and_mol - Tutorial}} | |||
== Task == | |||
Relaxation of the bond length of an oxygen dimer. | |||
== Input == | |||
=== {{TAG|POSCAR}} === | |||
O dimer in a box | O dimer in a box | ||
1.0 ! universal scaling parameters | 1.0 ! universal scaling parameters | ||
| Line 24: | Line 17: | ||
0 0 0 ! first atom | 0 0 0 ! first atom | ||
0 0 1.22 ! second atom | 0 0 1.22 ! second atom | ||
=== {{TAG|INCAR}} === | |||
{{TAGBL|SYSTEM}} = O2 dimer in a box | |||
{{TAGBL|ISMEAR}} = 0 ! Gaussian smearing | |||
{{TAGBL|ISPIN}} = 2 ! spin polarized calculation | |||
{{TAGBL|NSW}} = 5 ! 5 ionic steps | |||
{{TAGBL|IBRION}} = 2 ! use the conjugate gradient algorithm | |||
=== {{TAG|KPOINTS}} === | |||
Gamma-point only | |||
0 | |||
Monkhorst Pack | |||
1 1 1 | |||
0 0 0 | |||
== Calculation == | |||
*We have selected in the {{TAG|INCAR}} file that geometry relaxation should be performed. In this case 5 ionic steps ({{TAG|NSW}}=5) should be done at most. For the relaxation a conjugate gradient (CG) algorithm is used ({{TAG|IBRION}}=2). | |||
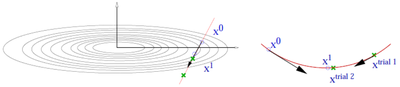
*The CG algorithm requires line minimizations along the search direction. This is done using a variant of Brent's algorithm. (Picture missing) | |||
**Trial step along search direction (gradient scaled by {{TAG|POTIM}}) | |||
**Quadratic or cubic interpolation using energies and forces at <math> \mathbf{x}_{0} </math> and <math> \mathbf{x}_{1} </math> allows to determine the approximate minimum | |||
**Continue minimization, if app. minimum is not accurate enough | |||
[[File:Fig O2 dimer 1.png|400px]] | |||
=== stdout === | |||
DAV: 1 0.517118590134E+02 0.51712E+02 -0.31393E+03 80 0.366E+02 | |||
... ... ... | |||
... ... ... | |||
DAV: 14 -0.985349953776E+01 -0.15177E-03 -0.57546E-06 64 0.125E-02 0.371E-03 | |||
DAV: 15 -0.985357023804E+01 -0.70700E-04 -0.22439E-06 64 0.741E-03 | |||
1 F= -.98535702E+01 E0= -.98535702E+01 d E =-.985357E+01 mag= 2.0000 | |||
curvature: 0.00 expect dE= 0.000E+00 dE for cont linesearch 0.000E+00 | |||
trial: gam= 0.00000 g(F)= 0.113E+00 g(S)= 0.000E+00 ort = 0.000E+00 (trialstep = 0.100E+01) | |||
search vector abs. value= 0.113E+00 | |||
bond charge predicted | |||
... ... ... | |||
... ... ... | |||
2 F= -.96234585E+01 E0= -.96234585E+01 d E =0.230112E+00 mag= 2.0000 | |||
trial-energy change: 0.230112 1 .order 0.190722 -0.113406 0.494850 | |||
step: 0.1397(harm= 0.1864) dis= 0.00731 next Energy= -9.861386 (dE=-0.782E-02) | |||
bond charge predicted | |||
... ... ... | |||
... ... ... | |||
3 F= -.98607735E+01 E0= -.98607735E+01 d E =-.720327E-02 mag= 2.0000 | |||
curvature: -0.09 expect dE=-0.900E-05 dE for cont linesearch -0.900E-05 | |||
trial: gam= 0.00000 g(F)= 0.969E-04 g(S)= 0.000E+00 ort =-0.331E-02 (trialstep = 0.828E+00) | |||
search vector abs. value= 0.969E-04 | |||
reached required accuracy - stopping structural energy minimisation | |||
Explanation of the output: | |||
*The quantitiy ''trial-energy change'' is the change of the energy in the trial step. | |||
*The first value after 1. order is the expected energy change calculated from the forces <math> ((\mathbf{F}(\textrm{start})+\mathbf{F}(\textrm{trial}))/2\times</math> change of positions - central difference. | |||
*The second and third value correspond to <math> \mathbf{F}(\mathrm{start}) \times</math> change of positions and <math> \mathbf{F} (\mathrm{trial}) \times </math> change of position. | |||
*The value ''step'' is the estimated size of the step leading to a line minimization along the current search direction. ''harm'' is the optimal step using a second order (or harmonic) interpolation. | |||
*The trial step size can be controlled by the paramter {{TAG|POTIM}} (the value ''step'' times the present {{TAG|POTIM}} is usually optimal). | |||
*The final positions after the optimization are stored in the {{TAG|CONTCAR}} file. One can copy {{TAG|CONTCAR}} to {{TAG|POSCAR}} and continue the relaxation. | |||
== Download == | == Download == | ||
[ | [[Media:Odimer.tgz| Odimer.tgz]] | ||
{{Template:At_and_mol}} | |||
[[Category:Examples]] | [[Category:Examples]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:16, 14 November 2019
Overview > O atom > O atom spinpolarized > O atom spinpolarized low symmetry > O dimer > CO > CO vibration > CO partial DOS > H2O >
H2O vibration > H2O molecular dynamics > Further things to try > List of tutorials
Task
Relaxation of the bond length of an oxygen dimer.
Input
POSCAR
O dimer in a box 1.0 ! universal scaling parameters 8.0 0.0 0.0 ! lattice vector a(1) 0.0 8.0 0.0 ! lattice vector a(2) 0.0 0.0 8.0 ! lattice vector a(3) 2 ! number of atoms cart ! positions in cartesian coordinates 0 0 0 ! first atom 0 0 1.22 ! second atom
INCAR
SYSTEM = O2 dimer in a box ISMEAR = 0 ! Gaussian smearing ISPIN = 2 ! spin polarized calculation NSW = 5 ! 5 ionic steps IBRION = 2 ! use the conjugate gradient algorithm
KPOINTS
Gamma-point only 0 Monkhorst Pack 1 1 1 0 0 0
Calculation
- We have selected in the INCAR file that geometry relaxation should be performed. In this case 5 ionic steps (NSW=5) should be done at most. For the relaxation a conjugate gradient (CG) algorithm is used (IBRION=2).
- The CG algorithm requires line minimizations along the search direction. This is done using a variant of Brent's algorithm. (Picture missing)
- Trial step along search direction (gradient scaled by POTIM)
- Quadratic or cubic interpolation using energies and forces at and allows to determine the approximate minimum
- Continue minimization, if app. minimum is not accurate enough
stdout
DAV: 1 0.517118590134E+02 0.51712E+02 -0.31393E+03 80 0.366E+02 ... ... ... ... ... ... DAV: 14 -0.985349953776E+01 -0.15177E-03 -0.57546E-06 64 0.125E-02 0.371E-03 DAV: 15 -0.985357023804E+01 -0.70700E-04 -0.22439E-06 64 0.741E-03 1 F= -.98535702E+01 E0= -.98535702E+01 d E =-.985357E+01 mag= 2.0000 curvature: 0.00 expect dE= 0.000E+00 dE for cont linesearch 0.000E+00 trial: gam= 0.00000 g(F)= 0.113E+00 g(S)= 0.000E+00 ort = 0.000E+00 (trialstep = 0.100E+01) search vector abs. value= 0.113E+00 bond charge predicted ... ... ... ... ... ... 2 F= -.96234585E+01 E0= -.96234585E+01 d E =0.230112E+00 mag= 2.0000 trial-energy change: 0.230112 1 .order 0.190722 -0.113406 0.494850 step: 0.1397(harm= 0.1864) dis= 0.00731 next Energy= -9.861386 (dE=-0.782E-02) bond charge predicted ... ... ... ... ... ... 3 F= -.98607735E+01 E0= -.98607735E+01 d E =-.720327E-02 mag= 2.0000 curvature: -0.09 expect dE=-0.900E-05 dE for cont linesearch -0.900E-05 trial: gam= 0.00000 g(F)= 0.969E-04 g(S)= 0.000E+00 ort =-0.331E-02 (trialstep = 0.828E+00) search vector abs. value= 0.969E-04 reached required accuracy - stopping structural energy minimisation
Explanation of the output:
- The quantitiy trial-energy change is the change of the energy in the trial step.
- The first value after 1. order is the expected energy change calculated from the forces change of positions - central difference.
- The second and third value correspond to change of positions and change of position.
- The value step is the estimated size of the step leading to a line minimization along the current search direction. harm is the optimal step using a second order (or harmonic) interpolation.
- The trial step size can be controlled by the paramter POTIM (the value step times the present POTIM is usually optimal).
- The final positions after the optimization are stored in the CONTCAR file. One can copy CONTCAR to POSCAR and continue the relaxation.